Navigating the Landscape of Acne: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Skincare
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Acne: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Skincare
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Acne: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Skincare. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of Acne: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Skincare

Acne, a common skin condition affecting millions worldwide, can be a source of significant distress and impact self-esteem. While it is often associated with adolescence, acne can persist into adulthood and manifest in various forms, from mild whiteheads and blackheads to severe cystic lesions. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of acne and adopting a comprehensive skincare regimen can significantly improve skin clarity and reduce breakouts.
Understanding Acne: A Complex Biological Process
Acne is a multifactorial condition, influenced by a complex interplay of biological factors. The primary cause lies in the overproduction of sebum, an oily substance produced by the sebaceous glands. This excess sebum, along with dead skin cells, can clog hair follicles, creating a breeding ground for the bacteria Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes). Inflammation ensues, leading to the characteristic red, inflamed lesions of acne.
Effective Skincare: A Multifaceted Approach
Effective acne management involves a multifaceted approach that addresses the underlying biological processes contributing to breakouts. This encompasses:
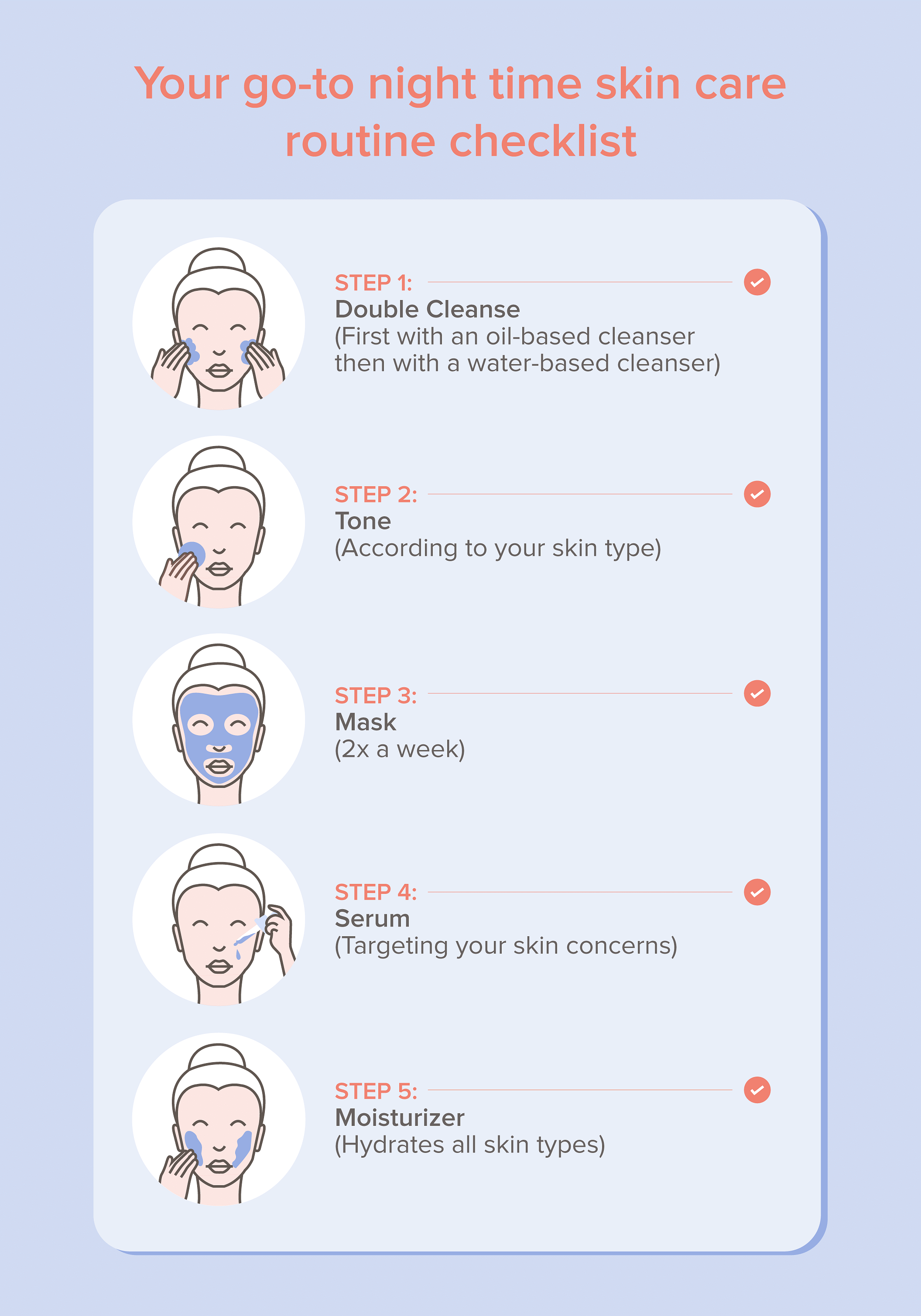
1. Cleansing: The Foundation of a Clean Canvas
- Gentle Cleansing: Employing a mild, non-comedogenic cleanser is crucial. Avoid harsh soaps or scrubs that can irritate the skin and exacerbate inflammation.
- Frequency: Wash your face twice daily, morning and evening, to remove dirt, oil, and sweat. Excessive washing can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and potential rebound oil production.
- Warm Water: Use lukewarm water, as hot water can further irritate the skin.
- Avoid Harsh Scrubs: Physical exfoliation with harsh scrubs can damage the skin barrier and worsen acne. Opt for chemical exfoliants like AHAs or BHAs, which can effectively remove dead skin cells without causing irritation.
2. Exfoliation: Unclogging the Pores
- Chemical Exfoliation: Alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) like glycolic acid and lactic acid are water-soluble and work by dissolving the bonds between dead skin cells, promoting cell turnover. Beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs) like salicylic acid are oil-soluble and penetrate deeper into the pores, effectively removing excess sebum and dead skin cells.
- Frequency: Start with a few times a week and gradually increase frequency as your skin tolerates it. Over-exfoliation can lead to dryness and irritation.
- Consider Your Skin Type: Choose an exfoliant appropriate for your skin type. Oily skin can tolerate more frequent exfoliation than dry skin.
3. Topical Treatments: Targeting the Acne-Causing Factors
- Benzoyl Peroxide: This over-the-counter medication effectively kills P. acnes bacteria and reduces inflammation. It is available in various concentrations, starting with 2.5% and increasing to 10%.
- Salicylic Acid: As mentioned previously, salicylic acid is a BHA that helps unclog pores and reduce inflammation. It is often combined with benzoyl peroxide for synergistic effects.
- Retinoids: Retinoids, derived from vitamin A, regulate cell turnover, reduce sebum production, and decrease inflammation. They can be obtained over-the-counter as retinol or by prescription as tretinoin.
- Sulfur: This natural ingredient can help absorb excess oil and reduce inflammation. It is often found in acne spot treatments.
- Tea Tree Oil: This essential oil has antibacterial properties that can help combat P. acnes bacteria.
4. Prescription Medications: Addressing Severe Cases
For severe acne that does not respond to over-the-counter treatments, a dermatologist may prescribe stronger medications, including:
- Oral Antibiotics: These medications target the bacteria that contribute to acne.
- Oral Isotretinoin: This powerful medication is reserved for severe, recalcitrant acne. It works by reducing sebum production and shrinking the sebaceous glands.
5. Lifestyle Modifications: Supporting Healthy Skin
- Diet: While there is no definitive evidence linking specific foods to acne, a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support overall skin health.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate acne. Techniques like exercise, meditation, or yoga can help manage stress levels.
- Sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for skin repair and rejuvenation. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
- Sun Protection: Sun exposure can worsen acne and lead to hyperpigmentation. Always use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
6. Professional Treatments: Complementary Solutions
- Chemical Peels: Chemical peels use acids to remove the outer layers of skin, promoting cell turnover and reducing acne lesions.
- Microdermabrasion: This procedure uses tiny crystals to gently abrade the skin, removing dead skin cells and improving texture.
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatments can target acne lesions and reduce inflammation.
FAQs on Effective Skincare for Acne
Q: How long does it take to see results from acne treatments?
A: It can take several weeks or even months to see significant improvement in acne. Patience and consistency are key.
Q: Can I use all acne treatments at the same time?
A: It is generally not recommended to use multiple strong acne treatments simultaneously, as this can lead to irritation and dryness. Consult a dermatologist for personalized guidance.
Q: What are the potential side effects of acne treatments?
A: Common side effects of acne treatments include dryness, redness, peeling, and irritation. These side effects are usually temporary and can be minimized by starting with low concentrations and gradually increasing as tolerated.
Q: Is it safe to use acne treatments during pregnancy?
A: Some acne treatments, particularly oral medications, are not safe for pregnant women. Always consult a dermatologist and your obstetrician before using any acne treatment during pregnancy.
Tips for Effective Acne Skincare
- Start Slowly: Introduce new products gradually to minimize the risk of irritation.
- Patch Test: Before applying any new product to your entire face, test it on a small area of skin first.
- Listen to Your Skin: Pay attention to how your skin reacts to different products and adjust your regimen accordingly.
- Be Consistent: Consistency is key to achieving lasting results. Stick to your skincare routine even when you are not experiencing breakouts.
- Seek Professional Guidance: If your acne is severe or persistent, consult a dermatologist for personalized advice and treatment options.
Conclusion: Empowering Skin Health Through Informed Skincare
Effective skincare for acne is a journey that requires understanding, patience, and consistency. By adhering to a comprehensive regimen that incorporates cleansing, exfoliation, topical treatments, and lifestyle modifications, individuals can effectively manage acne and achieve clear, healthy skin. Remember, seeking professional guidance from a dermatologist is crucial for personalized advice and treatment options tailored to individual needs. By taking a proactive approach to skincare, individuals can reclaim their confidence and enjoy the benefits of a clear complexion.


.jpg)





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Acne: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Skincare. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!