Unveiling The Science Behind Emollients: A Guide To Restoring Skin’s Natural Moisture Barrier
Unveiling the Science Behind Emollients: A Guide to Restoring Skin’s Natural Moisture Barrier
Related Articles: Unveiling the Science Behind Emollients: A Guide to Restoring Skin’s Natural Moisture Barrier
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Science Behind Emollients: A Guide to Restoring Skin’s Natural Moisture Barrier. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Science Behind Emollients: A Guide to Restoring Skin’s Natural Moisture Barrier
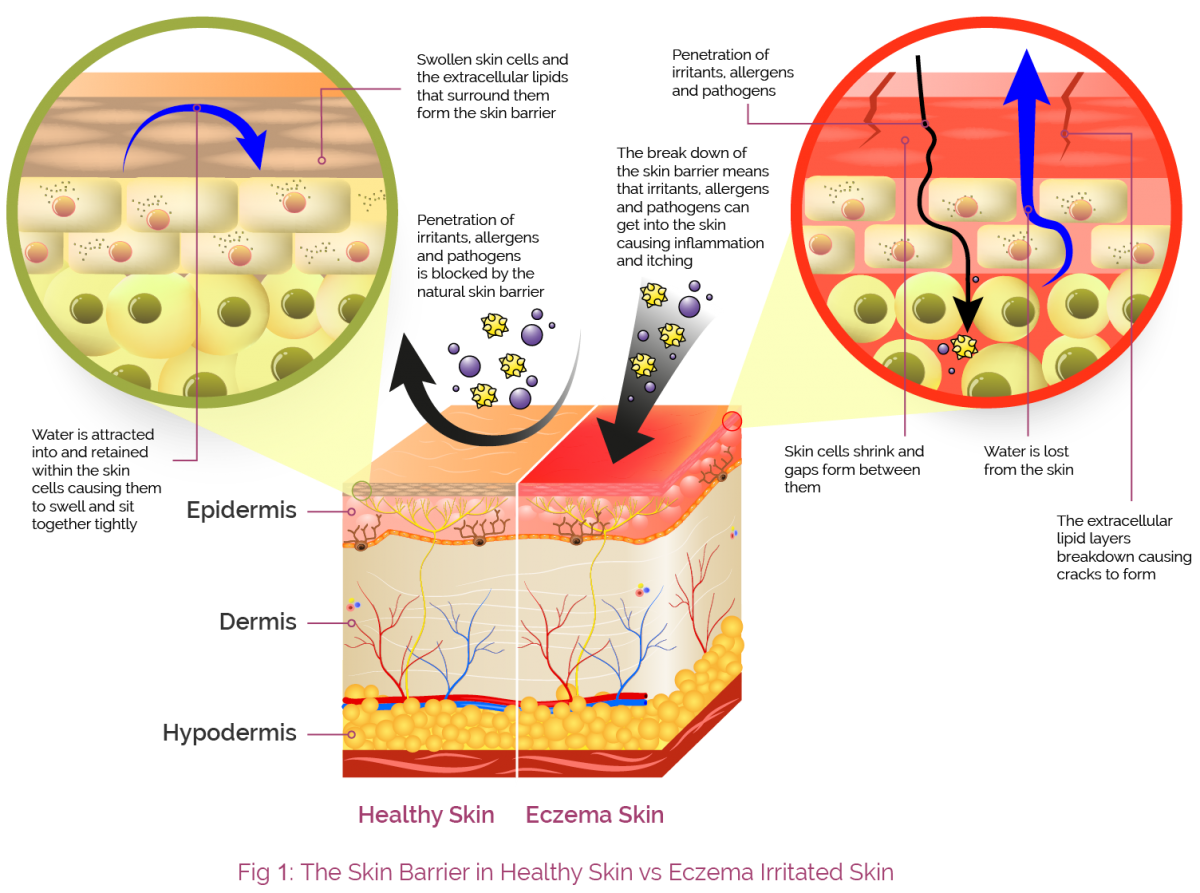
Dry skin, a common skin condition affecting individuals of all ages, is characterized by a lack of moisture, leading to a rough, flaky, and often itchy complexion. This dryness stems from a compromised skin barrier, the outermost layer of skin responsible for retaining moisture and protecting against environmental aggressors. While various factors contribute to dry skin, such as genetics, climate, and aging, the underlying culprit is often a deficiency in lipids, the natural fats that keep skin supple and hydrated.
Enter emollients, a class of skincare products designed to replenish these essential lipids and restore the skin’s natural moisture barrier. These products work by smoothing and softening the skin, providing a soothing effect and alleviating the discomfort associated with dryness.
Understanding the Science Behind Emollients
Emollients achieve their moisturizing effects through a multifaceted mechanism:
- Occlusion: Emollients act as a physical barrier, trapping moisture within the skin and preventing its evaporation. This occlusion is achieved by creating a thin, protective layer on the skin’s surface.
- Lipid Replenishment: Dry skin often suffers from a depletion of natural lipids, such as ceramides, cholesterol, and fatty acids. Emollients replenish these vital components, restoring the skin’s natural moisture barrier and promoting healthy skin function.
- Hydration Enhancement: Some emollients possess humectant properties, attracting and retaining moisture from the surrounding environment. This further enhances the skin’s hydration levels, contributing to a softer and smoother texture.
Types of Emollients
Emollients come in various forms, each with its unique properties and suitability for different skin types and needs:
- Oils: Oils, like mineral oil, coconut oil, and jojoba oil, are occlusive agents that create a protective layer on the skin, preventing moisture loss. They are often effective for very dry skin but can be comedogenic, meaning they may clog pores and contribute to breakouts in acne-prone individuals.
- Waxes: Waxes, such as beeswax and lanolin, are similar to oils in their occlusive properties but offer a more emollient feel. They are often used in lip balms and other products designed for sensitive skin.
- Fatty Acids: Fatty acids, including stearic acid, palmitic acid, and oleic acid, are key components of the skin’s natural lipids. They are commonly found in moisturizers and creams, providing both hydration and skin barrier repair.
- Humectants: Humectants, like hyaluronic acid and glycerin, attract and retain moisture from the environment. They are often used in combination with other emollients to enhance hydration and provide a more supple feel.
Choosing the Right Emollient
Selecting the appropriate emollient for your specific needs depends on several factors:
- Severity of Dryness: Mild dryness may respond well to lighter emollients like lotions, while severe dryness may require thicker creams or ointments.
- Skin Type: Oily or acne-prone skin may benefit from non-comedogenic emollients, while sensitive skin may require hypoallergenic and fragrance-free options.
- Individual Preferences: Some individuals may prefer the texture and feel of certain emollients over others. It is important to experiment and find what works best for your skin.
Benefits of Using Emollients
Regular use of emollients offers numerous benefits for individuals with dry skin:
- Improved Hydration: Emollients replenish the skin’s moisture barrier, leading to increased hydration and a softer, smoother complexion.
- Reduced Itch and Flaking: By restoring the skin’s protective layer, emollients alleviate the itching and flaking associated with dry skin.
- Enhanced Skin Barrier Function: Emollients strengthen the skin’s natural barrier, protecting it from environmental damage and promoting overall skin health.
- Improved Appearance: Hydrated skin appears healthier and more radiant, with a reduced appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
FAQs about Emollients for Dry Skin
Q: How often should I apply emollients?
A: The frequency of application depends on the severity of dryness and individual skin needs. Generally, applying emollients twice daily, morning and evening, is recommended.
Q: Are emollients safe for all skin types?
A: While emollients are generally safe for most skin types, individuals with acne-prone skin should choose non-comedogenic options. Sensitive skin may require hypoallergenic and fragrance-free emollients.
Q: Can emollients be used on babies and children?
A: Emollients are generally safe for babies and children, but it is essential to choose products specifically formulated for sensitive skin. Consult with a pediatrician for guidance.
Q: Can emollients cause breakouts?
A: Some emollients, particularly those containing heavy oils, can be comedogenic and contribute to breakouts in acne-prone individuals. It is important to choose non-comedogenic options or consult with a dermatologist for personalized recommendations.
Q: Can emollients be used in conjunction with other skincare products?
A: Emollients can be incorporated into a comprehensive skincare routine. Apply them after cleansing and before applying other products, such as serums or moisturizers.
Tips for Using Emollients Effectively
- Apply Emollients to Damp Skin: Applying emollients to slightly damp skin enhances their absorption and effectiveness.
- Use Gentle Massage: Gently massage the emollient into the skin to promote better absorption and circulation.
- Avoid Over-Exfoliation: Exfoliating too frequently can strip the skin of its natural oils and worsen dryness. Use emollients to restore moisture and avoid excessive exfoliation.
- Choose Products Free of Irritants: Opt for emollients that are hypoallergenic, fragrance-free, and free of common irritants like dyes and preservatives.
- Consult a Dermatologist: If you experience persistent dryness or irritation, consult with a dermatologist for personalized advice and treatment options.
Conclusion
Emollients play a crucial role in restoring and maintaining the skin’s natural moisture barrier, offering a solution for individuals struggling with dry skin. By replenishing essential lipids and providing a protective barrier, emollients effectively alleviate dryness, itching, and flaking, promoting a healthier and more radiant complexion. Choosing the right emollient for your specific needs and incorporating it into a comprehensive skincare routine can significantly improve the overall health and appearance of your skin. Remember, a well-hydrated skin is a happy skin.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cerave-6b9f7943e28e4664bb0c6d3fa16ced43.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/USED_Emollients-for-Skin-4108-1x1-hires-6733ccb3fa0c4bda8af234dda2f1a1b3.jpg)



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/CestMoi-78ff174defe04aa792c1e4c74a452d92.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Science Behind Emollients: A Guide to Restoring Skin’s Natural Moisture Barrier. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!