The Emerging World Of Electronic Skin: A Revolution In Human-Machine Interaction
The Emerging World of Electronic Skin: A Revolution in Human-Machine Interaction
Related Articles: The Emerging World of Electronic Skin: A Revolution in Human-Machine Interaction
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Emerging World of Electronic Skin: A Revolution in Human-Machine Interaction. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Emerging World of Electronic Skin: A Revolution in Human-Machine Interaction

The human skin, our largest organ, is a marvel of nature. It serves as a protective barrier, regulates temperature, and provides us with a sense of touch. But what if we could imbue artificial materials with similar capabilities? Enter electronic skin, a revolutionary technology that mimics the properties of human skin, opening up a world of possibilities in diverse fields.
Electronic skin, also known as e-skin, is a flexible, adaptable material equipped with an array of sensors that can detect pressure, temperature, strain, and even pain. This remarkable technology is not just a futuristic concept; it is rapidly evolving and finding applications in fields ranging from robotics and prosthetics to healthcare and wearable technology.
Unveiling the Essence of Electronic Skin
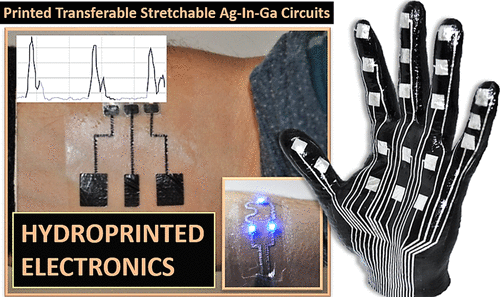
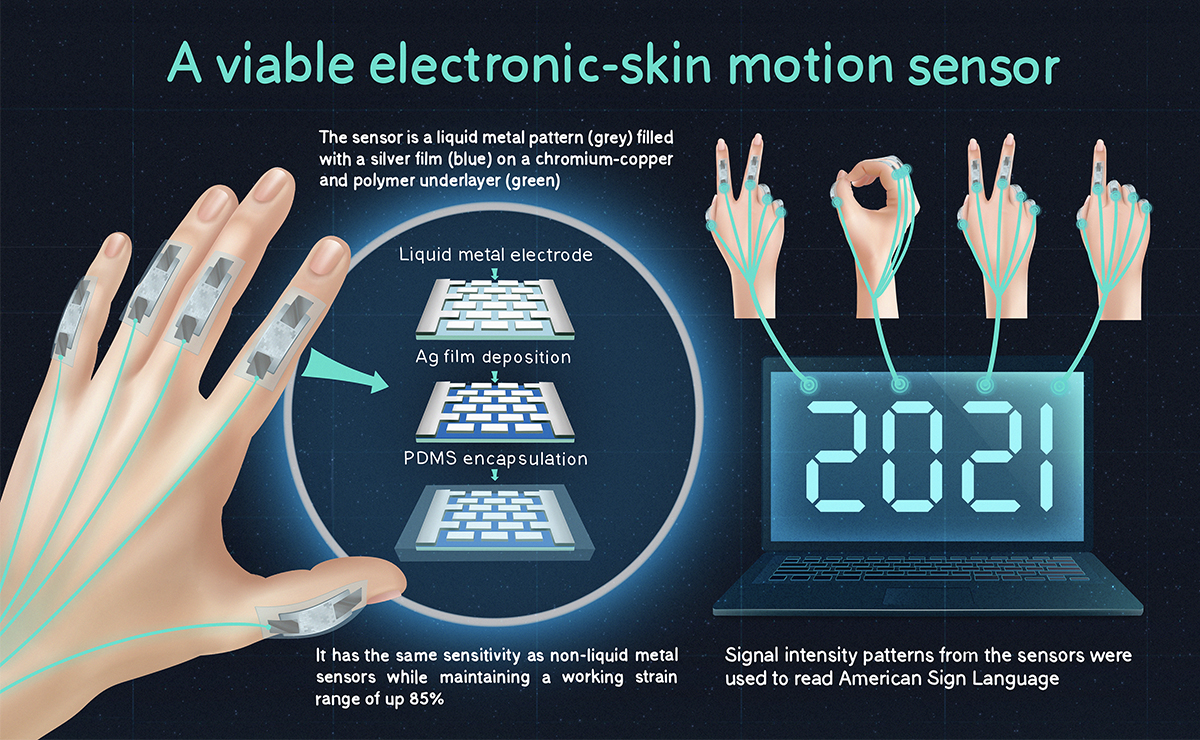
At its core, electronic skin consists of a network of sensors integrated onto a flexible substrate. These sensors, often composed of materials like graphene, carbon nanotubes, or conductive polymers, are designed to respond to external stimuli and translate them into electrical signals. These signals are then processed by an integrated circuit, providing real-time information about the surrounding environment.
Key Components of Electronic Skin:
- Sensors: These are the eyes and ears of electronic skin, detecting pressure, temperature, strain, and even chemical or biological changes.
- Substrate: The foundation upon which the sensors are mounted. This material needs to be flexible, durable, and compatible with the sensors.
- Interconnects: These conductive pathways facilitate the flow of electrical signals between sensors and the processing unit.
- Processing Unit: This component interprets the signals received from the sensors and translates them into meaningful information.
Applications of Electronic Skin: A Glimpse into the Future
The versatility of electronic skin makes it an ideal candidate for a wide range of applications, revolutionizing various industries:
1. Robotics and Prosthetics:
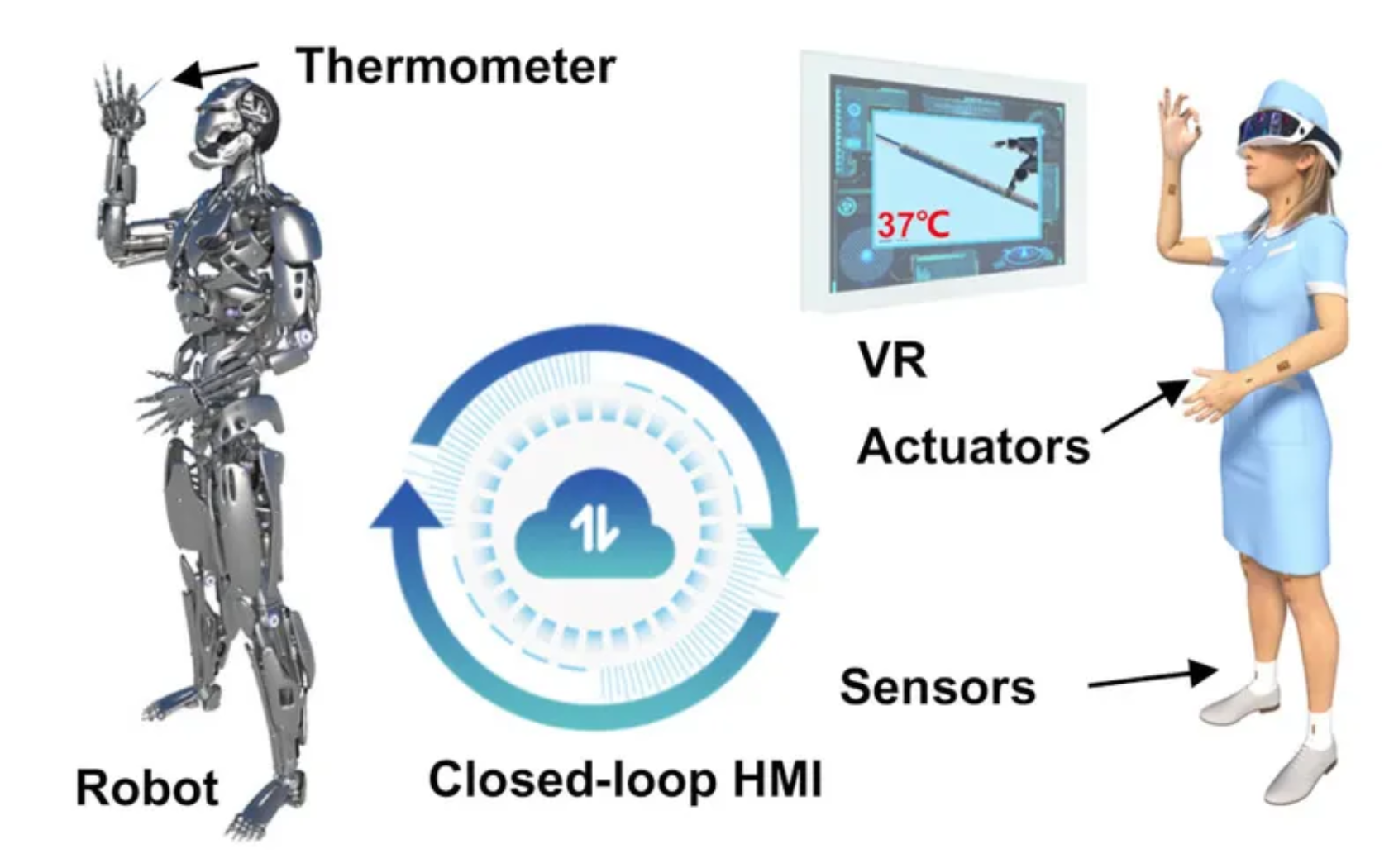
- Enhanced Human-Robot Interaction: E-skin allows robots to sense their environment and respond accordingly, enabling them to interact with humans more naturally and safely.
- Realistic Prosthetics: By incorporating e-skin, prosthetics can provide users with a sense of touch, improving their ability to manipulate objects and navigate their surroundings.
2. Healthcare:
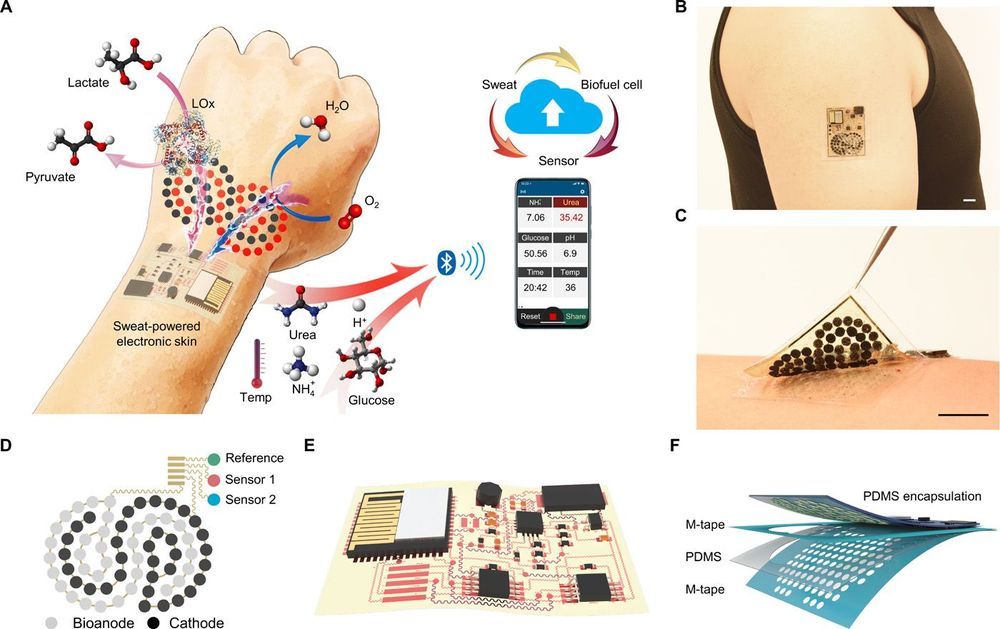
- Personalized Medicine: E-skin can monitor vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature in real-time, providing valuable data for personalized healthcare.
- Wound Healing and Monitoring: E-skin can be used to monitor wound healing progress and detect potential infections, facilitating faster recovery.
- Biomedical Devices: E-skin can be integrated into implantable devices, enabling continuous monitoring of internal organs and providing feedback for medical treatments.
3. Wearable Technology:
- Smart Clothing: E-skin can be incorporated into clothing to monitor fitness levels, track movement patterns, and even provide feedback on posture.
- Human-Computer Interfaces: E-skin can be used to create more intuitive and responsive interfaces for devices, allowing users to control them with gestures or touch.
4. Industrial Applications:
- Industrial Automation: E-skin can be used to monitor the condition of machinery and detect potential failures, preventing downtime and improving efficiency.
- Environmental Monitoring: E-skin can be deployed in harsh environments to monitor air quality, water pollution, and other environmental parameters.
Challenges and Future Directions
While electronic skin holds immense potential, several challenges need to be addressed before it can be widely adopted:
- Durability and Reliability: E-skin needs to be robust enough to withstand wear and tear in real-world conditions.
- Power Consumption: Efficient power management is crucial for long-term operation, especially for wearable applications.
- Integration and Scalability: Developing cost-effective methods for mass production and integration with existing systems is essential for widespread adoption.
Despite these challenges, research in electronic skin is progressing rapidly. Scientists are continuously developing new materials, sensors, and fabrication techniques to overcome these hurdles. The future holds exciting possibilities for electronic skin, as it promises to revolutionize human-machine interaction and transform various industries.
FAQs about Electronic Skin:
Q: What is the difference between electronic skin and artificial skin?
A: Artificial skin is primarily used for wound healing and tissue regeneration, focusing on replicating the biological functions of human skin. Electronic skin, on the other hand, focuses on mimicking the sensory capabilities of human skin, enabling it to detect and respond to external stimuli.
Q: Can electronic skin truly feel pain?
A: While electronic skin can detect pressure and temperature changes, it does not experience pain in the same way as humans. It simply converts these stimuli into electrical signals that can be interpreted by a processing unit.
Q: What are the potential ethical concerns surrounding electronic skin?
A: Ethical concerns surrounding electronic skin include potential privacy breaches, data security issues, and the potential for misuse in surveillance or manipulation. Careful consideration of these concerns is crucial as the technology evolves.
Q: What are the potential applications of electronic skin in the future?
A: Future applications of electronic skin could include:
- Biometric authentication: Using e-skin for secure identification based on unique physical characteristics.
- Augmented reality: Integrating e-skin with AR devices for more immersive and interactive experiences.
- Human-machine symbiosis: Creating seamless integration between humans and machines, enabling new levels of communication and collaboration.
Tips for Understanding Electronic Skin:
- Focus on the sensory capabilities: Electronic skin is primarily about sensing and responding to the environment, not simply mimicking the appearance of human skin.
- Consider the materials and fabrication techniques: The materials used in e-skin and the methods of fabrication play a crucial role in its performance and limitations.
- Explore the various applications: Electronic skin has diverse applications, ranging from healthcare to robotics, each with unique requirements and challenges.
Conclusion:
Electronic skin is a transformative technology with the potential to revolutionize various aspects of our lives. As research continues to advance, e-skin is poised to become an integral part of our future, enhancing human-machine interaction, improving healthcare, and unlocking new possibilities in diverse industries. By understanding the principles, applications, and challenges of electronic skin, we can better appreciate its profound impact on the world around us.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Emerging World of Electronic Skin: A Revolution in Human-Machine Interaction. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!