The Complexities Of Acne: A Comprehensive Guide
The Complexities of Acne: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: The Complexities of Acne: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Complexities of Acne: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Complexities of Acne: A Comprehensive Guide

Acne, a common skin condition affecting millions worldwide, is more than just a cosmetic concern. It can significantly impact self-esteem and social interactions. Understanding the intricate mechanisms behind acne is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and managing its impact. This article delves into the complex interplay of factors contributing to acne development, providing a comprehensive overview of its pathogenesis.
The Anatomy of Acne:
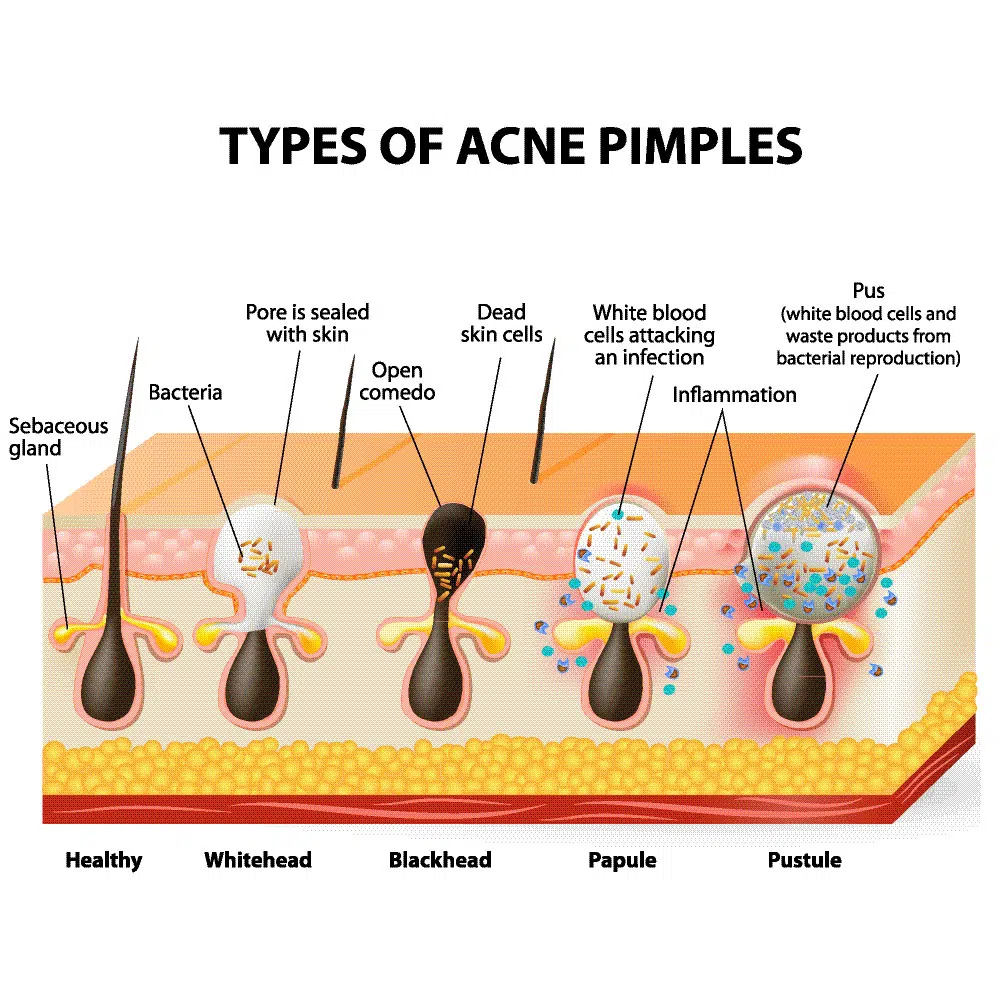
Acne originates in the pilosebaceous unit, a complex structure found in the skin. This unit comprises:
- Hair follicle: A small, tube-like structure that houses a hair shaft.
- Sebaceous gland: Connected to the hair follicle, this gland produces sebum, an oily substance that lubricates the skin and hair.
- Sebum: A mixture of lipids, waxes, and other components that forms a protective barrier on the skin’s surface.
The Genesis of Acne:
Acne arises from a combination of factors, including:
- Excess sebum production: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty, can trigger increased sebum production, leading to clogged hair follicles.
- Abnormal keratinization: The process of skin cell shedding is disrupted, causing dead cells to accumulate within the hair follicle, further obstructing its opening.
- Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes): This bacteria, normally present on the skin, thrives in the oily environment of clogged follicles. It produces inflammatory substances that contribute to the formation of acne lesions.
- Inflammation: The body’s immune response to P. acnes and other irritants triggers inflammation, leading to redness, swelling, and pain associated with acne.
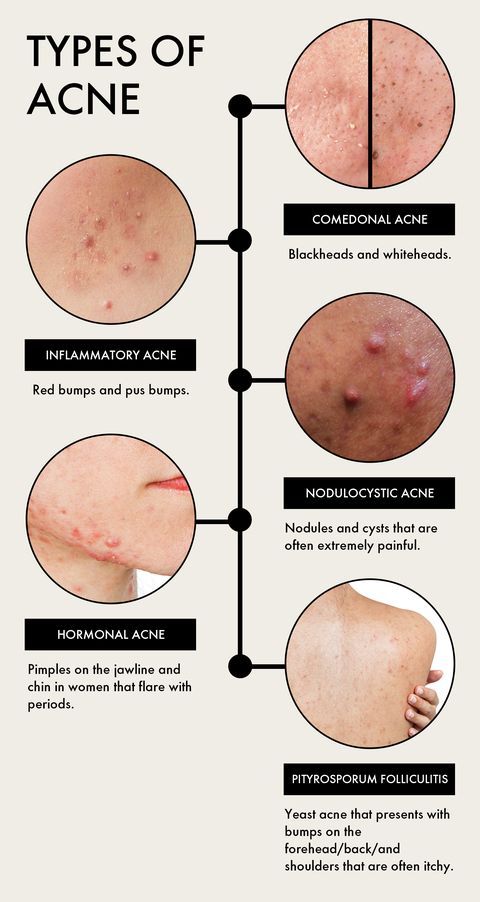
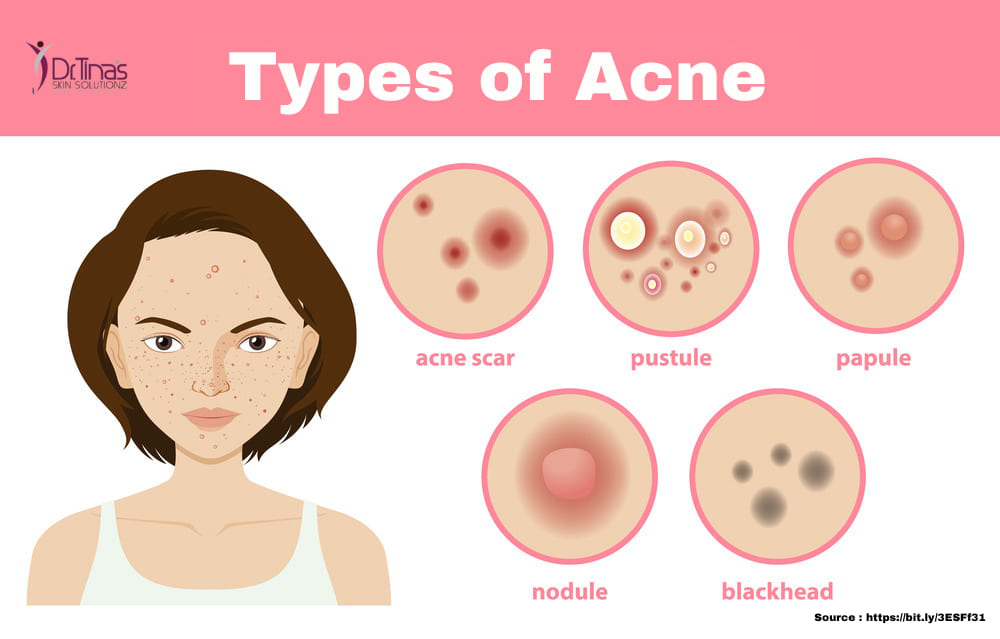
The Stages of Acne:
Acne progresses through various stages, each characterized by distinct clinical features:
- Comedones: These are the initial non-inflammatory lesions that form when a hair follicle becomes clogged with sebum and dead cells.
- Whiteheads: Closed comedones, where the follicle opening is completely blocked, appear as small, white bumps.
- Blackheads: Open comedones, where the follicle opening remains open, appear as black dots due to the oxidation of sebum.
- Papules: These are small, red, inflamed bumps caused by the body’s immune response to P. acnes.
- Pustules: These are larger, pus-filled bumps that develop when the inflammation extends deeper into the skin.
- Nodules: These are large, hard, and painful lesions that develop deep within the skin and can leave permanent scars.
- Cysts: These are large, pus-filled lesions that can cause significant inflammation and scarring.
The Role of Hormones:
Hormonal fluctuations play a significant role in acne development, particularly during puberty, pregnancy, and menstruation. Androgens, male sex hormones, stimulate sebaceous gland activity, leading to increased sebum production. This increased sebum production can contribute to clogged follicles and acne formation.
The Influence of Genetics:
Genetic predisposition also plays a crucial role in acne development. Individuals with a family history of acne are more likely to experience the condition. Specific genes have been linked to increased sebum production, abnormal keratinization, and inflammatory responses, all contributing to acne pathogenesis.
The Impact of Lifestyle:
Lifestyle factors can also influence acne severity. These include:
- Diet: While the link between diet and acne is not fully understood, some studies suggest that a diet high in processed foods, sugar, and dairy products may contribute to acne development.
- Stress: Stress can trigger hormonal changes that increase sebum production, potentially exacerbating acne.
- Skin care practices: Using harsh cleansers, scrubbing excessively, and applying heavy makeup can irritate the skin and worsen acne.
The Importance of Acne Treatment:
Acne treatment aims to reduce inflammation, prevent further breakouts, and minimize scarring. Treatment options include:
- Topical medications: These include retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, and salicylic acid, which work by reducing inflammation, unclogging pores, and killing bacteria.
- Oral medications: Antibiotics, hormonal medications, and isotretinoin are used for more severe acne.
- Light therapy: This involves exposing the skin to specific wavelengths of light to kill bacteria and reduce inflammation.
- Chemical peels: These involve applying a chemical solution to the skin to remove the top layer and promote cell turnover.
- Laser therapy: This uses a laser to target acne lesions and reduce inflammation.
FAQs about Acne:
Q: Is acne contagious?
A: No, acne is not contagious. It is caused by a combination of factors within the individual’s body, including hormonal fluctuations, genetic predisposition, and bacteria.
Q: What are the long-term effects of acne?
A: While most cases of acne resolve with treatment, some individuals may experience persistent acne or scarring. Scarring can be minimized with early and effective treatment.
Q: Can I prevent acne?
A: While acne is often influenced by factors beyond our control, there are steps we can take to minimize its severity:
- Maintain a healthy diet: Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and dairy products.
- Manage stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques like exercise, yoga, or meditation.
- Develop a gentle skin care routine: Use a mild cleanser, avoid harsh scrubbing, and choose non-comedogenic (non-pore-clogging) products.
Q: How can I prevent acne scars?
A: Early and effective treatment is crucial for minimizing scarring. If acne lesions are left untreated, they can become inflamed and lead to permanent scarring.
Conclusion:
Acne, a complex skin condition, arises from a multifaceted interplay of factors including hormonal fluctuations, genetic predisposition, bacteria, and lifestyle choices. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and managing its impact. While acne can be challenging, with appropriate treatment and preventative measures, individuals can achieve clearer skin and improve their overall well-being.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Complexities of Acne: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!