Navigating The Regulatory Landscape: A Guide To FDA Approval For Cosmetic Products
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape: A Guide to FDA Approval for Cosmetic Products
Related Articles: Navigating the Regulatory Landscape: A Guide to FDA Approval for Cosmetic Products
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Regulatory Landscape: A Guide to FDA Approval for Cosmetic Products. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape: A Guide to FDA Approval for Cosmetic Products

The cosmetics industry is a vibrant and dynamic sector, driven by innovation and consumer demand. However, the production and sale of cosmetics are not without their regulatory frameworks. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of cosmetics, thereby safeguarding public health. Understanding the regulatory landscape and navigating the approval process is paramount for any entity seeking to introduce a cosmetic product to the American market.
The FDA’s Role in Cosmetics Regulation:
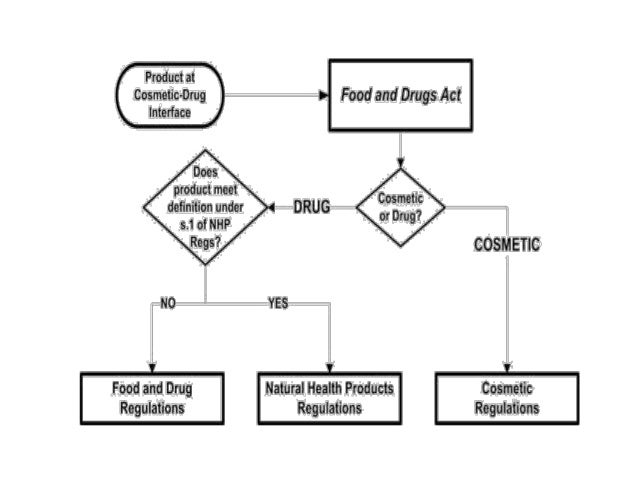
The FDA’s authority over cosmetics is rooted in the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act) of 1938, which sets forth broad guidelines for the safety and labeling of cosmetics. Unlike drugs, cosmetics are not subject to pre-market approval by the FDA. This means that manufacturers are generally responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before they are marketed. However, the FDA does have the authority to take action against unsafe or mislabeled cosmetics after they have been marketed.
Key Aspects of FDA Regulation:
The FDA’s regulatory framework for cosmetics encompasses several key aspects:
- Safety: The FD&C Act requires that cosmetics be safe when used as directed. This includes the responsibility of manufacturers to conduct appropriate testing and research to ensure their products do not pose unreasonable risks to consumers.
- Labeling: The FD&C Act mandates that cosmetic products bear accurate and informative labeling. This includes disclosing ingredients, directions for use, warnings, and any other relevant information necessary for consumers to make informed decisions.
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs): The FDA encourages manufacturers to follow GMPs, a set of principles that ensure the quality, safety, and consistency of manufactured products. While not mandatory for cosmetics, adherence to GMPs demonstrates a commitment to producing safe and reliable products, which can enhance consumer confidence.
- Adverse Event Reporting: The FDA encourages manufacturers to report any adverse events associated with their products, such as allergic reactions or other unexpected health issues. This information is critical for monitoring the safety of cosmetics and identifying potential risks.
Navigating the Approval Process:
While cosmetics do not require pre-market approval, the FDA actively monitors the market and may take action against products that pose safety risks. Manufacturers should proactively engage with the FDA to ensure compliance and avoid potential issues. This engagement can encompass several key steps:
1. Pre-Market Planning:
- Product Formulation and Development: The development of a cosmetic product should prioritize safety and efficacy. Manufacturers should conduct thorough research, including safety testing, to ensure their product meets the required standards.
- Labeling and Packaging: The labeling should be clear, accurate, and informative, adhering to FDA guidelines. This includes disclosing ingredients, directions for use, warnings, and any other relevant information.
- GMP Compliance: Manufacturers should adopt and implement GMPs to ensure the quality and consistency of their products. This demonstrates a commitment to producing safe and reliable cosmetics.
2. Communication and Transparency:
- FDA Consultation: Manufacturers can engage with the FDA through voluntary pre-market consultations to discuss product safety and labeling concerns. This can be beneficial in clarifying any potential issues and ensuring compliance before launching the product.
- Documentation and Records: Maintaining accurate records of product development, manufacturing, and testing is crucial. This documentation serves as evidence of compliance and can be essential in addressing any potential regulatory inquiries.
- Adverse Event Reporting: Establishing a robust system for reporting adverse events associated with the product is essential. Manufacturers should promptly report any adverse events to the FDA and maintain detailed records of these reports.
3. Post-Market Surveillance:
- Continuous Monitoring: Manufacturers should continue to monitor their products in the market for any potential safety issues or adverse events. This can involve conducting post-market surveillance studies, collecting consumer feedback, and reviewing reports from healthcare professionals.
- Responding to FDA Inquiries: Manufacturers should respond promptly and thoroughly to any inquiries from the FDA regarding their products. This includes providing relevant documentation and addressing any concerns raised by the agency.
- Product Recall: In the event of a safety concern, manufacturers should be prepared to initiate a product recall, working closely with the FDA to ensure the safety of consumers.
Benefits of FDA Compliance:
Adherence to FDA regulations for cosmetics offers several significant benefits:
- Enhanced Consumer Confidence: Consumers are more likely to trust products that have been developed and marketed in accordance with FDA regulations. This builds brand loyalty and strengthens the company’s reputation.
- Reduced Regulatory Risk: Compliance with FDA regulations minimizes the risk of regulatory action, such as product recalls, fines, or legal challenges. This provides stability and predictability for the business.
- Improved Product Quality: Adhering to GMPs and other regulatory standards enhances the quality and consistency of products, leading to improved consumer satisfaction and reduced product defects.
- Stronger Competitive Advantage: Compliance with FDA regulations can be a competitive advantage, allowing companies to differentiate themselves in the marketplace as a responsible and reliable producer of safe and effective products.
FAQs on FDA Approval for Cosmetics:
Q: Does the FDA approve cosmetics?
A: The FDA does not pre-approve cosmetics before they are marketed. However, the agency has the authority to take action against unsafe or mislabeled cosmetics after they are marketed.
Q: What are the key requirements for cosmetics under FDA regulations?
A: Key requirements include ensuring product safety, accurate labeling, and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs).
Q: What are some common safety concerns associated with cosmetics?
A: Common safety concerns include allergic reactions, skin irritation, and potential contamination.
Q: How can manufacturers ensure their products are safe?
A: Manufacturers should conduct thorough safety testing, including ingredient analysis, stability studies, and human clinical trials.
Q: What information should be included on cosmetic labels?
A: Labels should include ingredients, directions for use, warnings, and any other relevant information necessary for consumers to make informed decisions.
Q: How can manufacturers report adverse events associated with their products?
A: Manufacturers can report adverse events to the FDA through the Safety Reporting Portal or by contacting the agency directly.
Q: What are some tips for navigating the FDA regulatory landscape?
A: Manufacturers should engage with the FDA through voluntary pre-market consultations, maintain accurate documentation, and establish a robust system for reporting adverse events.
Conclusion:
Navigating the FDA regulatory landscape for cosmetics requires a proactive and informed approach. By understanding the key requirements, engaging with the agency, and prioritizing safety and compliance, manufacturers can establish a strong foundation for success in the American market. This not only safeguards public health but also fosters consumer trust and enhances the overall reputation of the cosmetics industry.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Regulatory Landscape: A Guide to FDA Approval for Cosmetic Products. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!