Healthcare In Jordan: A Comprehensive Overview
Healthcare in Jordan: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: Healthcare in Jordan: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Healthcare in Jordan: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Healthcare in Jordan: A Comprehensive Overview

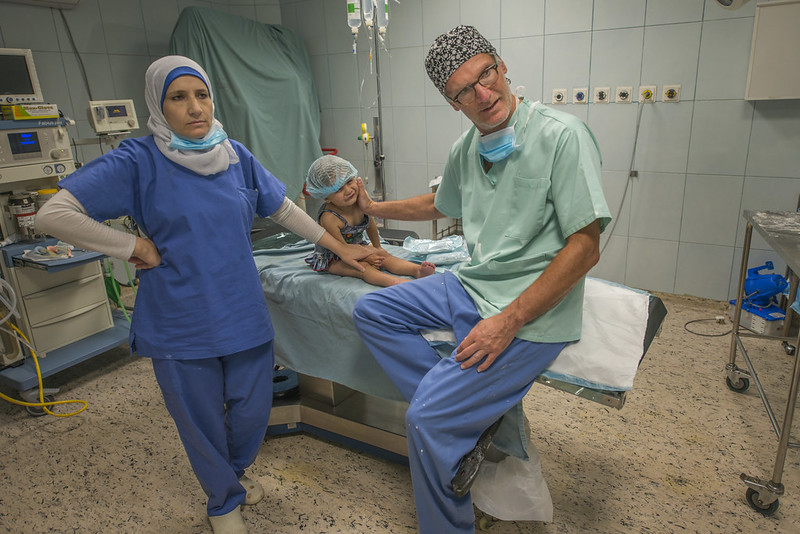
Jordan, a nation nestled in the heart of the Middle East, has made significant strides in developing its healthcare system over the past few decades. While challenges remain, the country boasts a network of public and private healthcare facilities, providing a range of services to its citizens and residents. This article provides a comprehensive overview of healthcare in Jordan, exploring its structure, key features, challenges, and future prospects.
The Healthcare Landscape: A Dual System
Jordan’s healthcare system operates on a dual structure, encompassing both public and private sectors. The Ministry of Health (MoH) oversees the public sector, which comprises government-run hospitals, clinics, and health centers. These facilities provide essential healthcare services to all citizens, regardless of their financial status, and are funded through taxes and government allocations.
The private sector, on the other hand, comprises a vibrant network of hospitals, clinics, and specialized medical centers. These facilities offer a wider range of services, including advanced medical technologies and specialized treatments. Private healthcare is largely funded through private insurance, out-of-pocket payments, and employer-sponsored plans.
Key Features of Jordan’s Healthcare System
Several key features distinguish Jordan’s healthcare system:
- Universal Healthcare Coverage: While not fully universal, Jordan’s healthcare system provides basic coverage to all citizens through the public sector. This ensures access to essential medical services, including preventive care, vaccinations, and treatment for common illnesses.
- Focus on Primary Care: The MoH emphasizes primary healthcare, aiming to prevent disease and promote health through community-based initiatives. This includes health education programs, screening campaigns, and early detection of health issues.
- Development of Specialized Centers: Jordan has invested in developing specialized medical centers for various conditions, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and ophthalmology. These centers offer advanced diagnostic and treatment options, attracting patients from neighboring countries.
- Emphasis on Quality: The MoH implements quality control measures and accreditation programs to ensure high standards of care across healthcare facilities. This includes rigorous training for medical professionals and continuous monitoring of medical practices.
- Technological Advancement: The healthcare sector in Jordan is embracing technology, incorporating telehealth, electronic health records, and advanced imaging techniques. This aims to enhance efficiency, improve patient care, and facilitate better access to specialized services.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its achievements, Jordan’s healthcare system faces several challenges:
- Unequal Access to Care: While the public sector provides basic healthcare, access to specialized treatments and advanced technologies is often limited, particularly for low-income populations.
- Financial Constraints: The healthcare system faces financial constraints, requiring ongoing investment to improve infrastructure, equipment, and staffing.
- Brain Drain: The shortage of skilled medical professionals, particularly specialists, is a persistent challenge, stemming from limited training opportunities and attractive job offers abroad.
- Growing Demand: Jordan’s healthcare system is challenged by a growing population and an aging demographic, leading to increased demand for services.
- Non-Communicable Diseases: The rise of non-communicable diseases, such as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer, poses a significant burden on the healthcare system, requiring increased investment in prevention and treatment.
To address these challenges, Jordan is actively pursuing several strategies:
- Investment in Infrastructure: The government is investing in upgrading existing facilities and constructing new hospitals and clinics to meet the growing demand.
- Training and Development: Efforts are underway to increase the number of medical professionals, particularly specialists, through scholarships, training programs, and partnerships with international institutions.
- Health Insurance Reform: The government is exploring ways to improve the health insurance system, making it more accessible and affordable for all citizens.
- Focus on Prevention: The MoH is implementing preventive healthcare programs, promoting healthy lifestyles, and encouraging early detection of health issues.
- Leveraging Technology: Jordan is exploring ways to utilize technology to improve healthcare delivery, enhance efficiency, and reduce costs.
Frequently Asked Questions about Healthcare in Jordan
Q: What are the main types of healthcare facilities in Jordan?
A: Jordan’s healthcare system comprises public and private facilities, including hospitals, clinics, specialized medical centers, and community health centers.
Q: What are the main healthcare services available in Jordan?
A: Healthcare services in Jordan encompass a wide range, including preventive care, vaccinations, treatment for common illnesses, specialized medical procedures, and advanced diagnostic services.
Q: How can I access healthcare in Jordan?
A: Citizens can access public healthcare facilities through the national health insurance scheme or by paying out-of-pocket. Private healthcare is accessed through private insurance, employer-sponsored plans, or by paying directly for services.
Q: What are the costs associated with healthcare in Jordan?
A: The cost of healthcare in Jordan varies depending on the type of facility, the service required, and the payment method. Public healthcare is generally subsidized, while private healthcare can be more expensive.
Q: What are the main health challenges facing Jordan?
A: Jordan faces several health challenges, including the rise of non-communicable diseases, limited access to specialized care, financial constraints, and a shortage of skilled medical professionals.
Tips for Navigating Healthcare in Jordan
- Understand the Healthcare System: Familiarize yourself with the structure of the healthcare system, including public and private facilities, insurance options, and payment methods.
- Choose a Reputable Facility: Opt for hospitals and clinics with a good reputation, accreditation, and experienced medical professionals.
- Consult with Your Doctor: Discuss your medical needs with your doctor and seek their advice on the appropriate healthcare facilities and services.
- Obtain Health Insurance: Consider obtaining health insurance, especially if you plan to access private healthcare or require specialized treatment.
- Be Proactive about Your Health: Engage in preventive care, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and undergo regular health screenings.
Conclusion
Jordan’s healthcare system is a complex and evolving landscape, characterized by a dual public and private structure. While challenges remain, the country has made significant progress in providing accessible and quality healthcare to its citizens. Ongoing investments in infrastructure, training, and technology are crucial to address the evolving needs of the population and enhance the quality of healthcare services. By embracing a holistic approach that prioritizes prevention, promotes innovation, and ensures equitable access to care, Jordan can further strengthen its healthcare system and contribute to the well-being of its people.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Healthcare in Jordan: A Comprehensive Overview. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!