E-Skins: A Revolution In Human-Machine Interaction
E-Skins: A Revolution in Human-Machine Interaction
Related Articles: E-Skins: A Revolution in Human-Machine Interaction
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to E-Skins: A Revolution in Human-Machine Interaction. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
E-Skins: A Revolution in Human-Machine Interaction

The realm of technology is constantly evolving, pushing the boundaries of what is possible and redefining our interactions with the digital world. One of the most captivating frontiers in this evolution is the development of electronic skins, or e-skins, a revolutionary technology that promises to bridge the gap between the physical and digital realms.
Unveiling the Essence of E-Skins
E-skins, also known as electronic skin, are thin, flexible, and adaptable materials that mimic the sensory capabilities and physical properties of human skin. These advanced materials are designed to seamlessly integrate with the human body, offering a range of functionalities that extend far beyond traditional human-machine interfaces.
A Multifaceted Technology
E-skins are not a singular technology but rather a multifaceted concept encompassing various components and functionalities:
- Sensors: E-skins incorporate a wide array of sensors, including pressure sensors, temperature sensors, strain sensors, and chemical sensors. These sensors enable the e-skin to perceive its environment and respond accordingly, providing real-time feedback on touch, temperature, pressure, and even chemical changes.
- Actuators: Actuators, often integrated within the e-skin, enable it to respond to stimuli by generating movement, vibration, or other forms of feedback. This allows for dynamic interaction with the environment, providing tactile sensations and creating a more immersive user experience.
- Electronics: E-skins are equipped with integrated electronics, including microprocessors, memory, and wireless communication capabilities. These electronics process sensor data, control actuators, and communicate with external devices, enabling the e-skin to perform complex tasks and interact with other technologies.
- Materials: E-skins are typically constructed from flexible and biocompatible materials, such as polymers, elastomers, and conductive inks. These materials allow for the creation of thin, lightweight, and conformable devices that can be comfortably worn on the skin.
The Power of Integration
The true power of e-skins lies in their ability to seamlessly integrate with the human body. This integration unlocks a wide range of possibilities across various fields:
- Healthcare: E-skins can revolutionize healthcare by enabling continuous and non-invasive monitoring of vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature. They can also be used for early detection of diseases, providing real-time feedback on skin conditions, muscle activity, and nerve function.
- Prosthetics and Robotics: E-skins can enhance the functionality of prosthetic limbs by providing sensory feedback and enabling more intuitive control. They can also be used to create robotic skins that can interact with the environment in a more human-like manner.
- Human-Computer Interaction: E-skins can transform human-computer interaction by providing a more intuitive and immersive user experience. Imagine controlling devices with gestures, receiving tactile feedback from virtual objects, or experiencing augmented reality through a second skin.
- Wearable Technology: E-skins can be incorporated into wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, to provide more accurate and personalized data on health, fitness, and activity levels. They can also be used to create smart clothing that can adapt to the wearer’s needs and environment.
- Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality: E-skins can enhance the immersive experience of augmented and virtual reality by providing tactile feedback and creating a more realistic sense of touch. This can be particularly useful for training simulations, gaming, and medical applications.
E-Skins: A Journey of Innovation
The development of e-skins is an ongoing journey of innovation, with researchers constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible. Here are some of the key challenges and advancements in the field:
- Improving Sensor Accuracy and Sensitivity: Researchers are working to improve the accuracy and sensitivity of the sensors used in e-skins, enabling them to detect even subtle changes in the environment.
- Developing More Powerful and Efficient Electronics: The integration of more powerful and efficient electronics is crucial for enabling complex functionalities and extending the battery life of e-skins.
- Ensuring Biocompatibility and Safety: As e-skins are intended for close contact with the human body, it is essential to ensure their biocompatibility and safety. Researchers are exploring new materials and fabrication methods to minimize potential risks.
- Developing Advanced Fabrication Techniques: The fabrication of e-skins requires specialized techniques that can create thin, flexible, and multi-layered structures. Researchers are continuously developing new methods to improve the efficiency and scalability of e-skin production.
- Addressing Ethical Considerations: The widespread adoption of e-skins raises ethical considerations regarding privacy, security, and the potential for misuse. It is essential to develop ethical guidelines and regulations for the development and use of e-skin technology.
FAQs about E-Skins
Q: What are the key benefits of using e-skins?
A: E-skins offer numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Human-Machine Interaction: E-skins provide a more intuitive and immersive way to interact with technology, bridging the gap between the physical and digital worlds.
- Improved Healthcare: E-skins enable continuous and non-invasive monitoring of vital signs, facilitating early disease detection and personalized healthcare.
- Enhanced Prosthetics and Robotics: E-skins can enhance the functionality of prosthetic limbs and create more human-like robotic systems.
- Increased Wearable Technology Capabilities: E-skins can be incorporated into wearable devices to provide more accurate and personalized data on health, fitness, and activity levels.
- Immersive Augmented and Virtual Reality Experiences: E-skins can enhance the immersive experience of augmented and virtual reality by providing tactile feedback.
Q: What are the potential risks associated with e-skins?
A: While e-skins hold immense potential, there are also potential risks associated with their use:
- Privacy Concerns: E-skins can collect sensitive personal data, raising concerns about privacy and data security.
- Security Risks: E-skins could be vulnerable to hacking or manipulation, potentially leading to security breaches.
- Ethical Considerations: The widespread adoption of e-skins raises ethical considerations regarding the potential for misuse and the impact on human autonomy.
- Health and Safety: It is essential to ensure the biocompatibility and safety of e-skin materials and designs to minimize potential health risks.
Q: How are e-skins currently being used?
A: E-skins are currently being used in various applications, including:
- Medical Monitoring: E-skins are being used to monitor vital signs, such as heart rate and blood pressure, and detect skin conditions.
- Prosthetics: E-skins are being integrated into prosthetic limbs to provide sensory feedback and enhance control.
- Robotics: E-skins are being used to create more human-like robotic systems that can interact with the environment in a more intuitive way.
- Wearable Technology: E-skins are being incorporated into smartwatches, fitness trackers, and other wearable devices to provide more accurate and personalized data.
- Research and Development: E-skins are being used extensively in research and development to explore new applications and improve the technology.
Q: What are the future prospects for e-skins?
A: The future of e-skins is bright, with ongoing research and development leading to:
- More Advanced and Sophisticated Features: E-skins are expected to become more sophisticated, incorporating advanced sensors, actuators, and electronics to provide a wider range of functionalities.
- Wider Range of Applications: E-skins are expected to find applications in a growing number of fields, including healthcare, robotics, entertainment, and education.
- Increased Affordability and Accessibility: As production techniques improve, e-skins are expected to become more affordable and accessible to a wider audience.
Tips for E-Skin Development and Implementation
- Focus on User Needs: The development of e-skins should be driven by a deep understanding of user needs and preferences.
- Prioritize Biocompatibility and Safety: Ensuring the biocompatibility and safety of e-skin materials and designs is paramount.
- Develop Robust and Reliable Electronics: The integration of robust and reliable electronics is essential for the functionality and longevity of e-skins.
- Address Ethical Considerations: It is crucial to address ethical considerations related to privacy, security, and the potential for misuse.
- Promote Collaboration and Open Innovation: Collaboration and open innovation are essential for driving progress in the field of e-skins.
Conclusion: A Future Embracing the Skin
E-skins represent a transformative technology with the potential to reshape our interactions with the world. By seamlessly integrating with the human body, they offer a wide range of possibilities across various fields, from healthcare and prosthetics to human-computer interaction and wearable technology. As research and development continue, e-skins are poised to play an increasingly important role in our lives, shaping a future where the boundaries between the physical and digital realms are blurred, and human-machine interaction reaches new heights of sophistication.
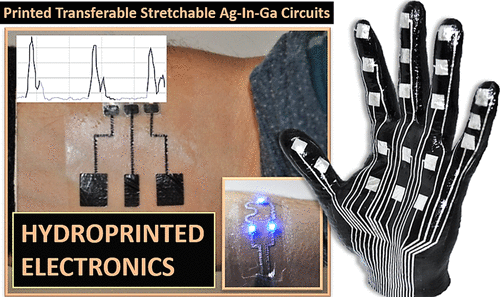

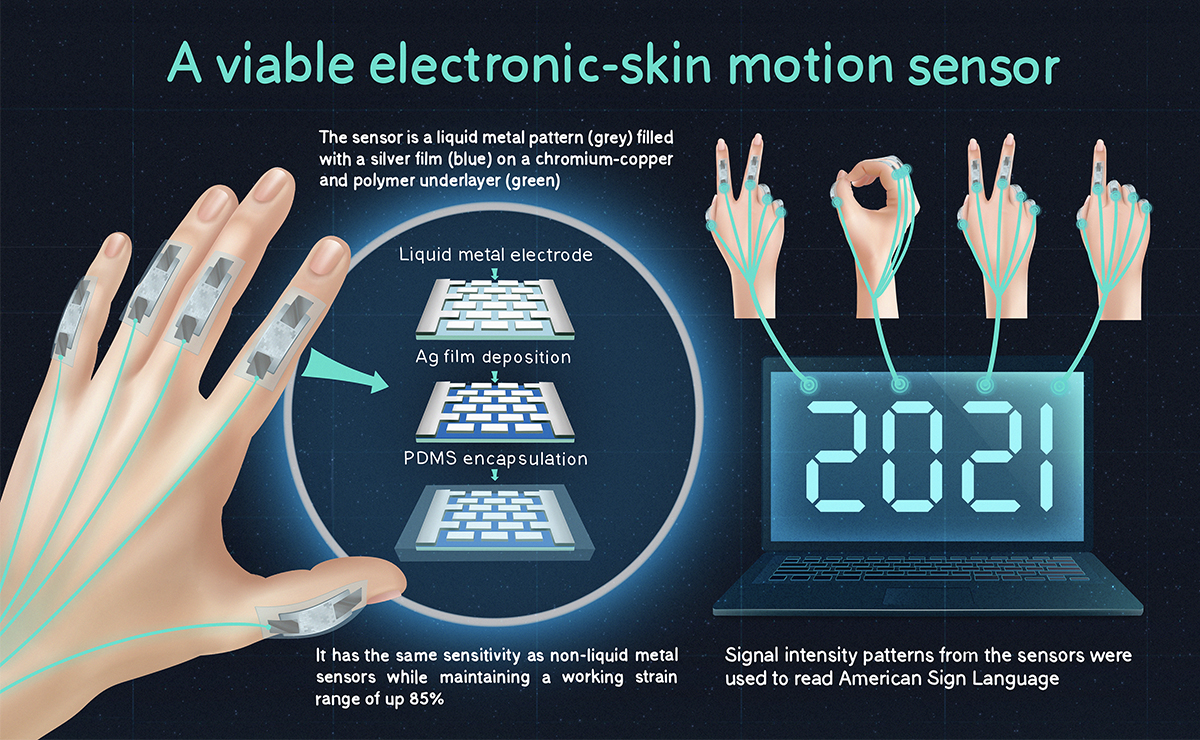




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into E-Skins: A Revolution in Human-Machine Interaction. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
