A Breakthrough In Wound Healing: The FDA Approval Of Synthetic Skin
A Breakthrough in Wound Healing: The FDA Approval of Synthetic Skin
Related Articles: A Breakthrough in Wound Healing: The FDA Approval of Synthetic Skin
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Breakthrough in Wound Healing: The FDA Approval of Synthetic Skin. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Breakthrough in Wound Healing: The FDA Approval of Synthetic Skin
The year 2000 marked a significant milestone in the field of medicine with the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of synthetic skin. This innovative technology, a testament to the relentless pursuit of medical advancement, revolutionized the treatment of severe burns and other challenging wounds.
The Genesis of Synthetic Skin:
The concept of synthetic skin, a bioengineered material designed to mimic the structure and function of natural skin, emerged from the urgent need for effective wound healing solutions. Traditional treatments for severe burns, often involving extensive skin grafting, presented numerous challenges: limited availability of donor skin, high risk of infection, and prolonged recovery periods.
Scientists and engineers, driven by the desire to address these limitations, embarked on a quest to create a viable alternative. Their efforts culminated in the development of synthetic skin, a multi-layered material composed of biocompatible materials that effectively support the healing process.
The Composition and Function of Synthetic Skin:
Synthetic skin, in its most basic form, consists of two primary layers:
- The outer layer: This layer, often composed of silicone or a similar material, acts as a protective barrier, shielding the wound from external contaminants and facilitating moisture retention.
- The inner layer: This layer, typically made of collagen or other biocompatible materials, provides a scaffold for the growth of new skin cells. It encourages the formation of new blood vessels and promotes the migration of cells from the wound edges, ultimately leading to the closure of the wound.
The FDA Approval and its Impact:
The FDA approval of synthetic skin in 2000 was a watershed moment, signifying the culmination of years of rigorous research and development. This approval marked a significant shift in the treatment paradigm for severe burns and other complex wounds, offering patients a more effective and less invasive alternative to traditional methods.
Benefits of Synthetic Skin:
The approval of synthetic skin brought numerous benefits to patients:
- Improved wound healing: Synthetic skin effectively promotes the formation of new skin cells, leading to faster and more complete wound closure.
- Reduced risk of infection: The protective outer layer of synthetic skin acts as a barrier against bacterial contamination, minimizing the risk of infection.
- Minimized pain and discomfort: Compared to traditional skin grafting, synthetic skin application is less invasive and generally associated with reduced pain and discomfort.
- Enhanced cosmetic outcomes: Synthetic skin often results in better cosmetic outcomes compared to traditional methods, minimizing scarring and promoting a more natural appearance.
- Increased availability of treatment: Synthetic skin offers a more readily available treatment option compared to traditional skin grafting, which relies on limited donor skin availability.
The Evolution of Synthetic Skin:
Since its initial approval, synthetic skin technology has continued to evolve, with researchers exploring new materials and refining existing formulations. These advancements have led to the development of synthetic skin products with enhanced properties, including:
- Improved biocompatibility: Newer generations of synthetic skin exhibit enhanced biocompatibility, minimizing the risk of rejection and promoting faster integration with the surrounding tissue.
- Enhanced functionality: Some synthetic skin products incorporate additional functionalities, such as the release of growth factors or antibiotics, further enhancing their therapeutic efficacy.
- Tailored applications: Research is underway to develop synthetic skin products tailored to specific wound types, offering more targeted treatment options.
FAQs about Synthetic Skin:
1. Is synthetic skin a permanent solution?
Synthetic skin is not a permanent solution. It serves as a temporary scaffold that encourages the growth of new skin. As the wound heals, the synthetic skin is gradually replaced by the patient’s own skin.
2. Does synthetic skin cause allergic reactions?
While synthetic skin is generally well-tolerated, allergic reactions can occur in rare cases. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the suitability of synthetic skin for individual patients.
3. How long does it take for synthetic skin to heal a wound?
The healing time varies depending on the size and severity of the wound. However, synthetic skin generally promotes faster healing compared to traditional methods.
4. Is synthetic skin covered by insurance?
Insurance coverage for synthetic skin treatment varies depending on the individual insurance plan. It is recommended to contact the insurance provider to clarify coverage details.
5. Are there any side effects associated with synthetic skin?
While synthetic skin is generally safe, potential side effects can include redness, itching, and swelling at the application site. These side effects are typically mild and resolve on their own.
Tips for Using Synthetic Skin:
- Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions: It is crucial to follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider regarding the application, care, and removal of synthetic skin.
- Keep the wound clean and dry: Maintain a clean and dry environment around the wound to prevent infection.
- Avoid direct sunlight: Protect the wound from direct sunlight, as it can delay healing.
- Avoid scratching or picking at the wound: Resist the urge to scratch or pick at the wound, as this can disrupt the healing process and increase the risk of infection.
- Monitor for any signs of infection: Keep a close eye on the wound for any signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, pain, or drainage. If you notice any of these signs, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Conclusion:
The FDA approval of synthetic skin in 2000 marked a pivotal moment in wound care, offering patients a revolutionary alternative to traditional treatments. This innovative technology has significantly improved wound healing outcomes, minimized the risk of infection, and reduced pain and discomfort for patients. The ongoing research and development in synthetic skin continue to push the boundaries of medical innovation, paving the way for even more effective and personalized wound healing solutions in the future.
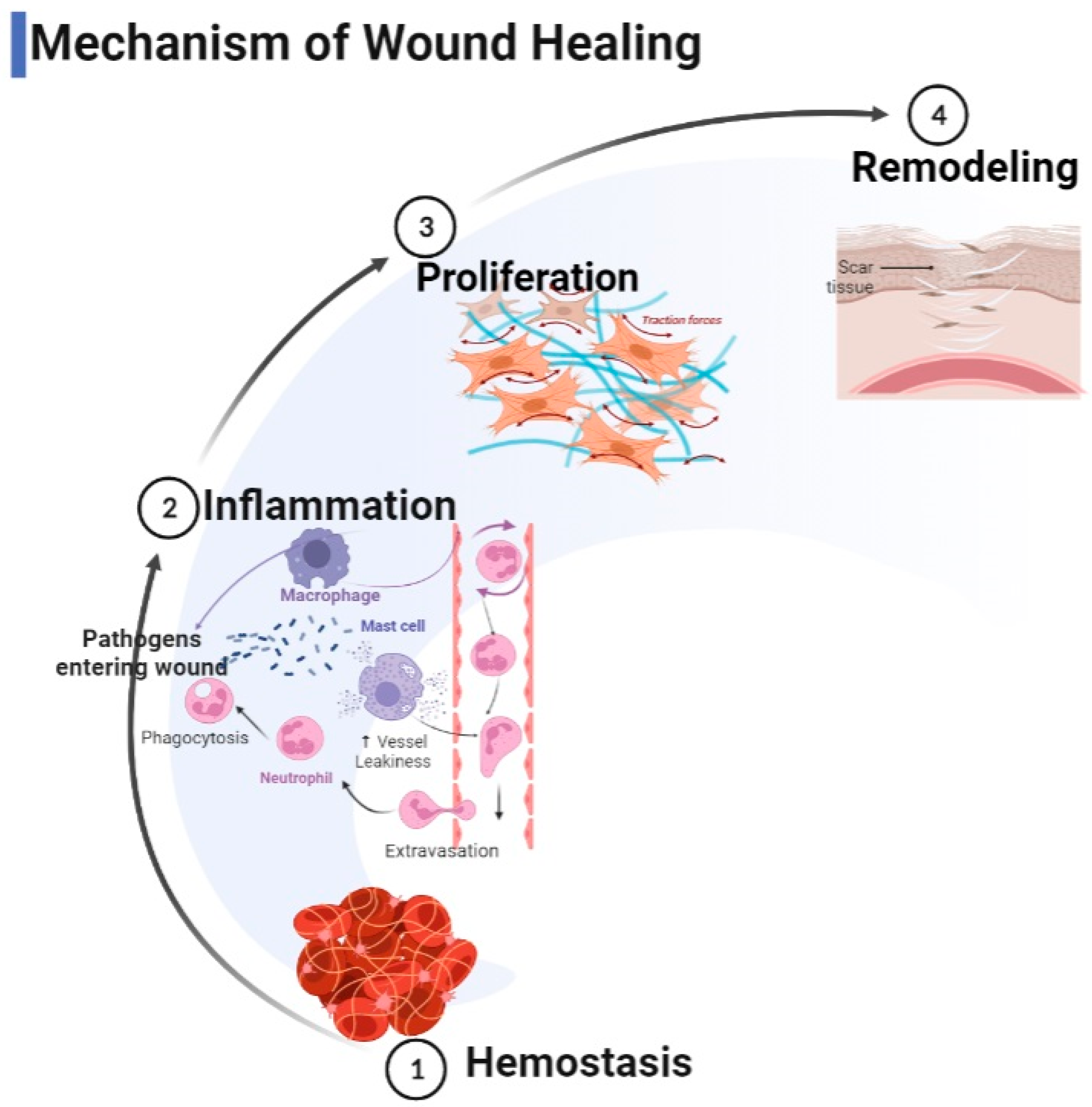
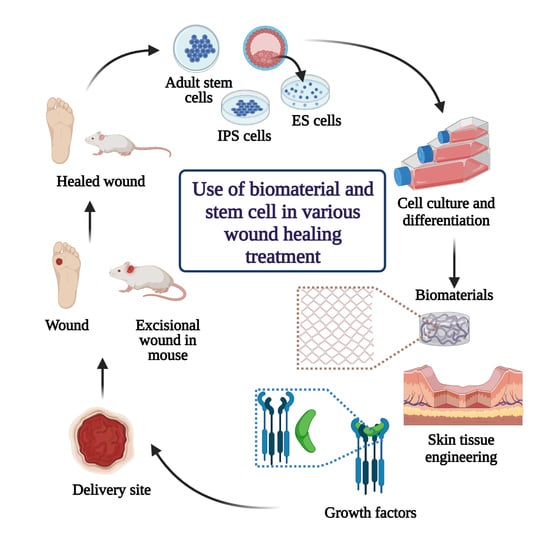





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Breakthrough in Wound Healing: The FDA Approval of Synthetic Skin. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
